Research Development Production We are a leading supplier to the global Life Science industry with solutions and services for research, biotechnology development and production, and pharmaceutical drug therapy development and productionStructure, properties, spectra, suppliers and links for spiramycin III Firstly, the photoinduced degradation of the five neonicotinoids was monitored and analyzed The ct curves recorded as mass area versus irradiation time are shown in Fig 1The ct curves are respresented as normalized concentrations, since the determination of transformation product concentrations was not possible due to individual ionization efficiencies and to the
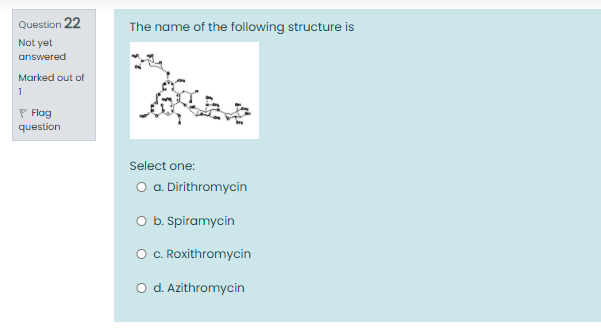
Solved 21 What Is The Name Of The Following Structure It Chegg Com
Spiramycin chemical structure
Spiramycin chemical structure-Spiramycin works best when there is a constant amount in the blood To help keep the amount constant, do not miss any doses Also, it is best to take the doses at evenly spaced times day and night If this interferes with your sleep or other daily activities, or if you need help in planning the best times to take your medicine, check with your Spiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide discovered in 1952 as a product of Streptomyces ambofaciens that has been available in oral formulations since 1955, and parenteral formulations since 1987 Resistant organisms include Enterobacteria, pseudomonads, and moulds



Monographie Spiramycine Adipate Stabilis 4 0
Spiramycin (Formacidine) is a 16membered ring macrolide (antibiotic) Spiramycin reduces the hygromycin A protections of nucleotides in 23 S rRNA 1 Spiramycin, a 16membered macrolide, inhibits translocation by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits with an apparent 11 stoichiometry Spiramycin acts primarily by stimulating theTroleandomycin used in Italy and Turkey;Spiramycin, hexanedioate (11) (salt) The 'Substance identity' section is calculated from substance identification information from all ECHA databases The substance identifiers displayed in the InfoCard are the best available substance name, EC number, CAS number and/or the molecular and structural formulas Some substance identifiers may
– Spiramycin does not penetrate into the CSF – It passes into breast milk and binds with plasma proteins (approximately 10%) Metabolism Spiramycin is slowly inactivated in the liver, with formation of unknown metabolites Excretion – Biliary elimination is very extensive;CHEBI spiramycin II A macrolide antibiotic produced by various Streptomyces species This entity has been manually annotated by the ChEBI Team No supplier information found for this compound A molecular entity capable of accepting a hydron from a donor (Br o nsted acid) A drug used to treat or prevent bacterial infectionsSpiramycin approved in the EU, and in other countries;
Transplacental transfer of spiramycin was investigated in a rhesus monkey model to study whether the antibiotic reaches therapeutic levels in the fetus Spiramycin concentrations were measured by bioassay and highperformance liquid chromatography Pharmacokinetic parameters were determined for bioactive spiramycin as measured by the bioassayAlthough spiramycin and neospiramycin residues were quantified in liver tissue samples with incurred residues, and a mean recovery of % for spiramycin and 80% for neospiramycin determined, residue concentrations above the limits of quantification 0 m g/kg for spiramycin and 100 m g/kg for neospiramycin were measured in only 5 out of 16Spiramycin adipate C49H84N2O18 CID structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological
/4ECE7900D4445432802585F90081B95E/$file/FS44433_structure.png)



Spiramycin Adipate 680 55 7 Biosynth Carbosynth Product



2
Acetylspiramycin C45H76N2O15 CID structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological The usual dose is 25 mg (75,000 IU) per kg (114 mg per pound) of body weight two times a day, or 17 mg (51,000 IU) per kg (77 mg per pound) of body weight three times a day Adults and teenagers—500 mg (1,500,000 IU) injected slowly into a vein every eight hours For severe infections, the dose is 1 gram (3,000,000 IU) injected slowly into As a member of the wwPDB, the RCSB PDB curates and annotates PDB data according to agreed upon standards The RCSB PDB also provides a variety of tools and resources Users can perform simple and advanced searches based on annotations relating to sequence, structure and function These molecules are visualized, downloaded, and analyzed by users who




Acetyl Spiramycin Biochemical Mybiosource




Regulation Of The Biosynthesis Of The Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Journal Of Bacteriology
Structure, properties, spectra, suppliers and links for Spiramycin ISpiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide antibiotic from Streptomyces ambofaciens It inhibits bacterial protein synthesis at the level of peptidytRNA dissociation from ribosomes It is mainly used against Grampositive bacteriaDrugscom provides accurate and independent information on more than 24,000 prescription drugs, overthecounter medicines and natural products This material is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment Data sources include IBM Watson Micromedex (updated 1 July 21), Cerner Multum™ (updated 1 July 21), ASHP



Macrolides Rapidly Inhibit Red Blood Cell Invasion By The Human Malaria Parasite Plasmodium Falciparum Bmc Biology Full Text




Spiramycin Rovamycine Macrolide Antibiotic Cas 8025 81 8 Ab Abcam
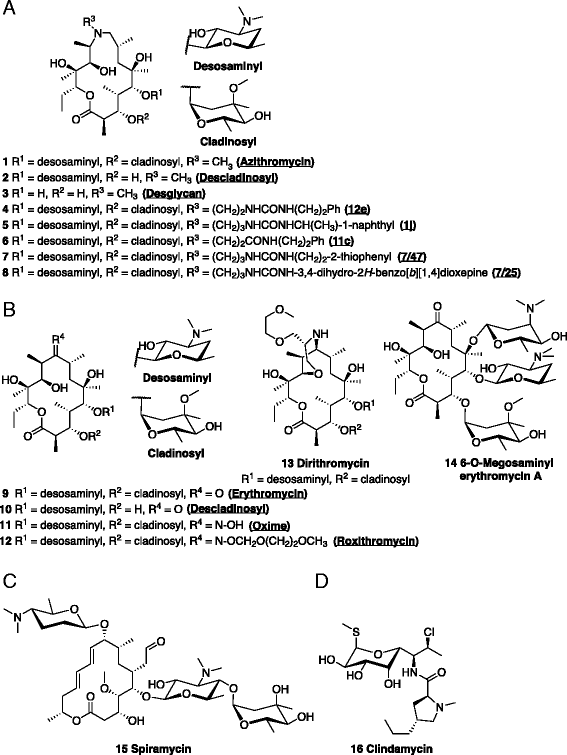
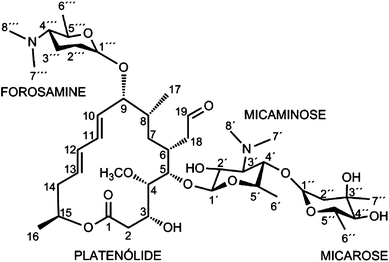
Were identified and their structure confirmed by mass spectrometry Residues of parent drug accounted for 04 mg/kg, while residues of spiramycin adducts with Lcysteine represented 105 mg/kg, and neospiramycin adducts with Lcysteine accounted forContains contains spiramycin adipate 1 500 000iu/g major major slow downs at usps and others, shipping times on checkout page from carriers are only estimates!Spiramycin (Rovamycin) is a macrolide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces ambofaciens with against bacteria and Toxoplasma gondii activities, and also has antiparasitic effect Spiramycin is composed of a 16member lactone ring, on which three sugars (mycaminose, forosamine, and mycarose) are attached Mechanism of Action & Protocol



Www Tandfonline Com Doi Pdf 10 1080 17




Antibiotics J Ppt Download
Chemical structure macrolide Application Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic that is commonly used to treat infections of soft tissues It has been used to treat bronchopulmonary infections in adults and has been used to study septicemia in mice Biochem/physiol ActionsSpiramycin II is a macrolide antibiotic produced by various Streptomyces species It has a role as an antibacterial drug, an antimicrobial agent and a bacterial metabolite It is an aldehyde, a disaccharide derivative, an ether, a macrolide, a tertiary amino compound and an acetate esterSpiramycin can also be used to treat infections caused by other kinds of bacteria However, it is not routinely used because many diseasecausing bacteria has acquired resistance to it Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic, and it belongs to the same class with the antibiotics Erthromycin, Azithromycin, and Telithromycin



Scheme 1 Adenine Nucleotide Recognition By Spiramycin And Some Of Its Aromatic Derivatives Springerlink




Spiramycin 90 0 Tci America Fisher Scientific
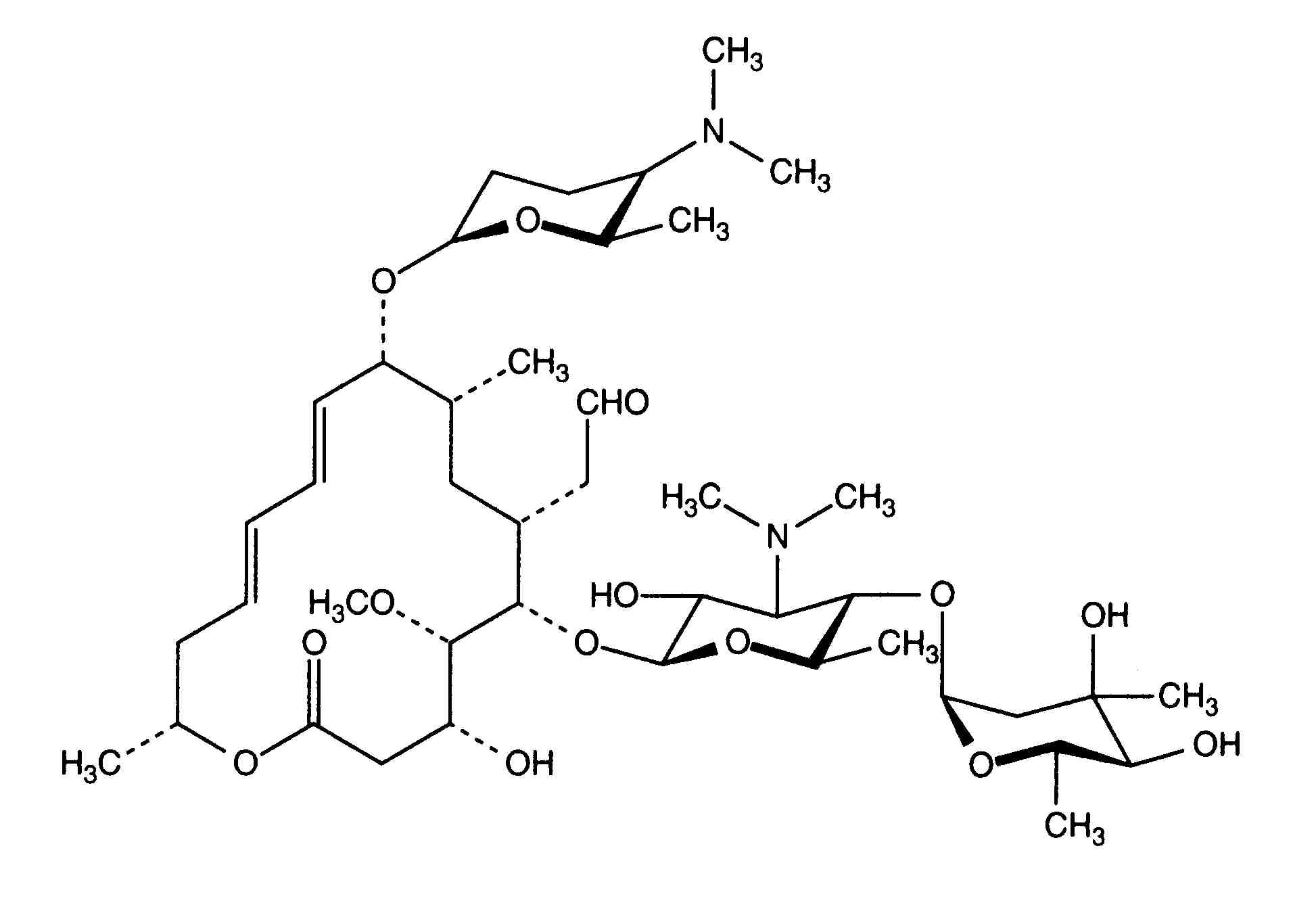
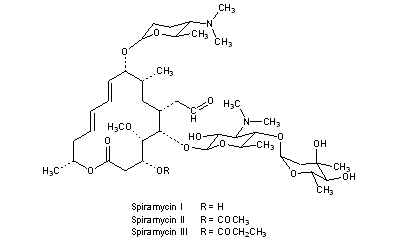
Spiramycin I ChEBI ID CHEBI Definition A macrolide antibiotic produced by various Streptomyces species that is used to treat toxoplasmosis and various other infections of soft tissues Stars This entity has been manually annotated by the ChEBI Team Secondary ChEBI IDsSpiramycin is a complex formed by three major components (I–III), which differ in the substituent at position 3 of the lactone nucleus The spiramycins are more stable than erythromycin A in an acidic medium Roxithromycin is highly stable at pH 42 (Figure 1414) Clarithromycin is 6Omethylerythromycin A, and the hydroxyl at position 11Spiramycin is used to treat many kinds of infections It is often used to treat toxoplasmosis in pregnant women since this medicine decreases the chance that the unborn baby will get the infection This medicine may also be used for other problems as determined by your doctor It will not work for colds, flu, or other virus infections
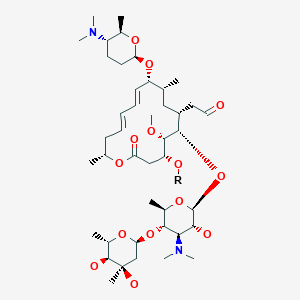



Spiramycin スピラマイシン Drug Approvals International
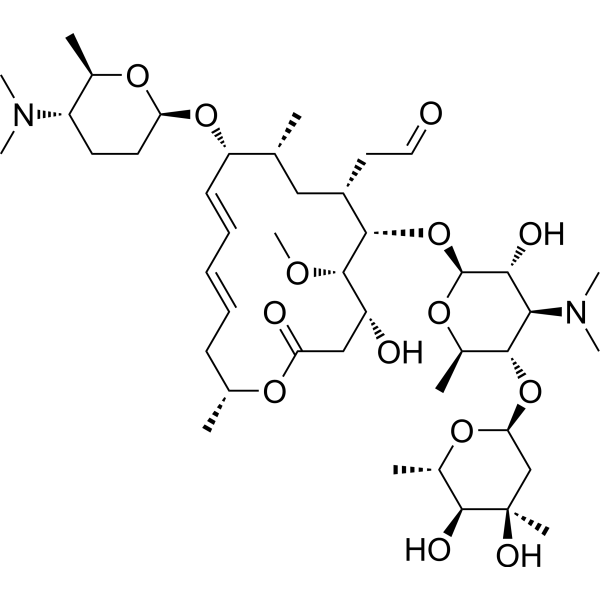



Spiramycin Rovamycin Antibiotic Medchemexpress
Structure, properties, spectra, suppliers and links for Spiramycin I,Spiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide It was isolated in 1954 as a product of Streptomyces ambofaciens by PINNERTSINDICO As a preparation for oral administration it has been used since 1955, in 1987 also the parenteral form was introduced into practice Since the introduction of spiramycin, thousands of patients have been treated with the drug and few have developed severe adverse reactions Gastrointestinal disorders were usually mild and transient, and allergic reactions were quite uncommon Liver injury was described only once and drug interactions have not been reported The safety profile of this




Neo Spiramycin I Cas 62 2 Neo Spiramycin I Supplier




Structures Of Spiramycins Neospiramycins Spiramycins U And S And Download Scientific Diagram
Spiramycin (SPY) is a macrolide antibacterial that is used similarly to erythromycin in the treatment of susceptible bacterial infections It has also been used, alone or in combination with MNZ, in the protozoal infections, cryptosporidiosis and toxoplasmosis ( 1 )Tylosin/tylocine used in animals;Research Development Production We are a leading supplier to the global Life Science industry with solutions and services for research, biotechnology development and production, and pharmaceutical drug therapy development and production




Effect Of Spiramycin And Tulathromycin On Abomasal Emptying Rate In Milk Fed Calves Abstract Europe Pmc
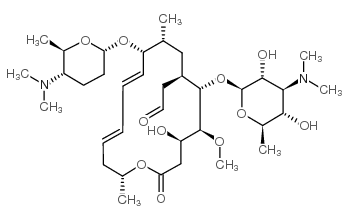



Neo Spiramycin I Cas 62 2 Chemsrc
Spiramycin Regulatory process names 2 IUPAC names 2 Other identifiers 1 Molecular structure The molecular structure is based on structures generated from information available in ECHA's databases If generated, an InChI string will also be generated and made available for searching This information is only displayed if the substance Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic and antiparasitic It is used to treat toxoplasmosis and various other infections of soft tissues Although used in Europe, Canada and Mexico, spiramycin is still considered an experimental drug in the United States, but can sometimes be obtained by special permission from the FDA for toxoplasmosis in the firstSpiramycin manufacturer in India Exporter in India Spiramycin 15 million iu,Spiramycin 3 million iu Largest Generic Manufacturer,drugs,Formula,producing Spiramycin MSDS,COA,pdf,doc chemical api method according to the present Spiramycin invention Suppliers List,Molecular Structure,Weight,IUPAC,Synonyms for Spiramycin




Spiramycin I 50 5 Wiki
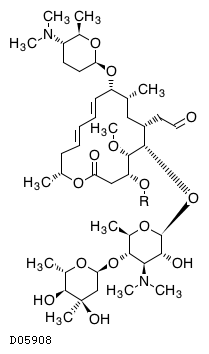



Kegg Drug Spiramycin
Crystal structures of the Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit complexed with the 16membered macrolide antibiotics carbomycin A, spiramycin, and tylosin and a 15membered macrolide, azithromycin, show that they bind in the polypeptide exit tunnel adjacent to the peptidyl transferase center An antibiotic used for the treatment and control of a number of bacterial and mycoplasmal infections in animals and also used as a growth promotor Availability status Introduction & key dates 00, Europe Examples of species treated Poultry, Sheep, Cattle, Pigs, Cats, Dogs Chemical structure IsomerismPLQDGTZICFBBSODPUAUXBSSAN Spiramycin adipate Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information



Q Tbn And9gcth3d8x1nireuodgfhyz04qsitlwdy5u24hqn3wfh7gfdgiknay Usqp Cau




Spiramycin I 50 5
Abstract Crystal structures of the Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit complexed with the 16membered macrolide antibiotics carbomycin A, spiramycin, and tylosin and a 15membered macrolide, azithromycin, show that they bind in the polypeptide exit tunnel adjacent to the peptidyl transferase center RAYMOND and SERGE (1965) studied the structure of spiramycin by means of hydrolysis products of spiramycin, It was demonstrated that rnycaminose, isomycamine, as well as the acetylated spiramycin 2 and propionylated spiramycin 4 residues, are attached direct to the chain of the antibiotic Mycarose, however, is attached to mycarninose by anMessage from usps alert usps is experiencing unprecedented package increases and limited employee availability due to the impacts of covid19 we appreciate your patience and remain




Cas 50 5 Spiramycin I Lookchem




Spiramycin C43h74n2o14 Spiramycin I R H Bertin Bioreagent
Ketolides Ketolides are a class of antibiotics that are structurally related to the macrolides They are used to treat respiratory tract infections caused by macrolideresistant bacteriaSpiramycin is a complex formed by three major components (I–III), which differ in the substituent at position 3 of the lactone nucleus The spiramycins are more stable than erythromycin A in an acidic medium Roxithromycin is highly stable at pH 42 (Figure 1414)Levels are 15 to 40 times higher than those in serum




Spiramycin Embonate Cas 08 7 Glentham Life Sciences
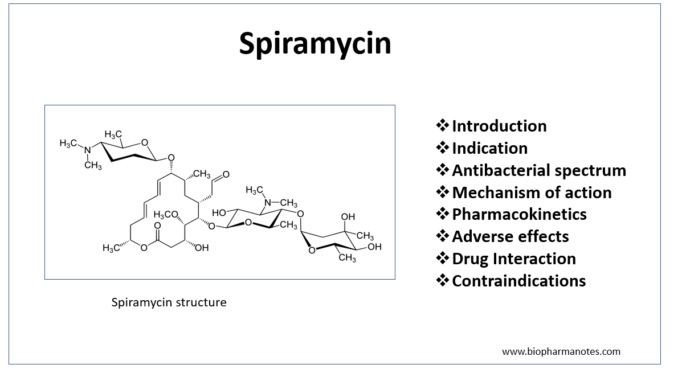



Pharmacology Of Spiromycin Biopharma Notes
Spiramycin Article in French Lamy L, Landry RG, Roy S Chemotherapeutic agents appear to offer a great potential in the treatment of periodontal disease in conjunction with root planning and/or surgical approach One of these chemotherapeutic agents is spiramycinSpiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide (antibiotic) It was discovered in 1952 as a product of Streptomyces ambofaciens As a preparation for oral administration it has been used since 1955, in 1987 also the parenteral form was introduced into pr Read More Please waitAbstract Spiramycin was less active than erythromycin in vitro against sensitive strains of Staphylococcus aureus, but was as effective against staphylococcal infections in mice when the drugs were administered immediately after infection spiramycin was relatively more effective in prophylactic experiments when the antibiotics were administered at 4 or at 6 hr before infection



Spiramycin 8025 81 8



Academic Oup Com Jac Article Pdf 16 Suppl A 1 16 Suppl A 1 Pdf
Spiramycin is a macrolide originally discovered as product of Streptomyces ambofaciens, with antibacterial and antiparasitic activities Although the specific mechanism of action has not been characterized, spiramycin likely inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome




Solved 21 What Is The Name Of The Following Structure It Chegg Com




Structure Activity Relationships Of Ketolides Vs Macrolides Douthwaite 01 Clinical Microbiology And Infection Wiley Online Library




Spiramycin 8025 81 8




Spiramycin Biorbyt
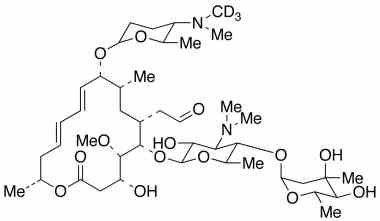



Spiramycin Impurities Pharmaffiliates



Spiramycin Drug Monograph Druginfosys Com




Macrolide Antibiotics In The Treatment Of Asthma An Update Allergologia Et Immunopathologia



Spiramycin Formacidine Cas 8025 81 8 Abmole Bioscience Spiramycin Price




5hh Bxdld 7 Fm




Structure Activity Relationships Of Ketolides Vs Macrolides Clinical Microbiology And Infection




A Chemical Structure Of Spiramycin Pk 7 9 B Dose Dependent Download Scientific Diagram



Spiramycin I C43h74n2o14 Chemspider




Antibiotics Having A B Lactam Ring Prezentaciya Onlajn



Search Q Rovamycine Tbm Isch




Rcsb Pdb 1kd1 Co Crystal Structure Of Spiramycin Bound To The 50s Ribosomal Subunit Of Haloarcula Marismortui
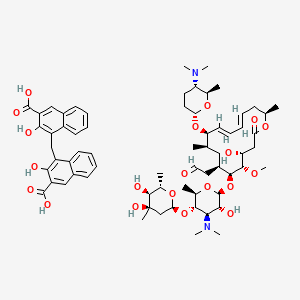



Spiramycin Embonate C66h90n2o Pubchem
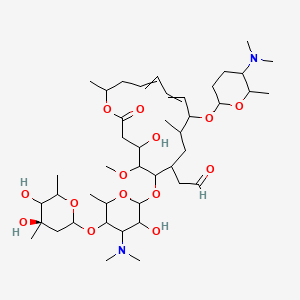



Rovamycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem




Espiramicina Wikipedia La Enciclopedia Libre




Spiramycin Biorbyt
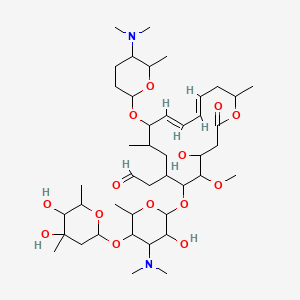



Spiramycin スピラマイシン Drug Approvals International



Tables And Figures



Spiramycin




Acetyl Spiramycin Spiramycin Adipate Spiramycin Base Manufacturers And Suppliers Price Fengchen
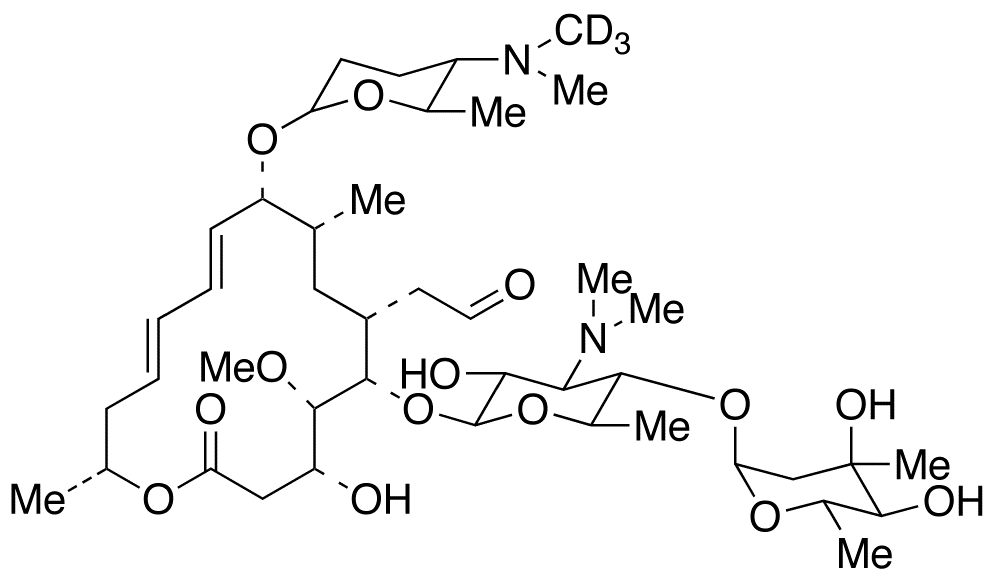



Spiramycin I D3 9 O 2r 5s 6r 5 Dimethylamino Tetrahydro 6 Methyl 2h Pyran 2 Yl Leucomycin V D3 Foromacidin A D3 Spiramycin A D3 C H D N O Trc
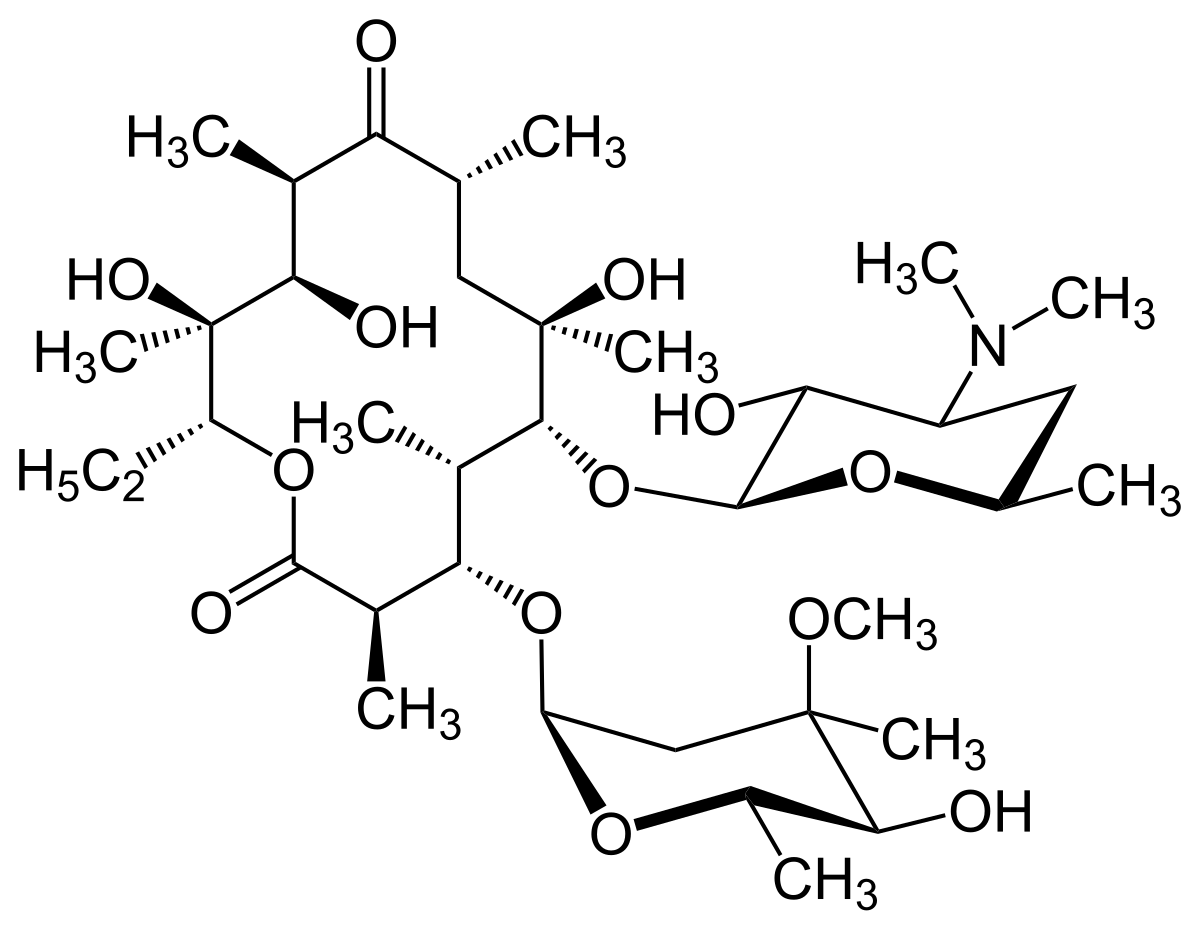



Macrolide Wikipedia




Acetyl Spiramycin Biochemical Mybiosource




Rovamycine Spiramycin Buy Online




Spiramycin Adipate Cas 680 55 7 Antibiotic Medkoo
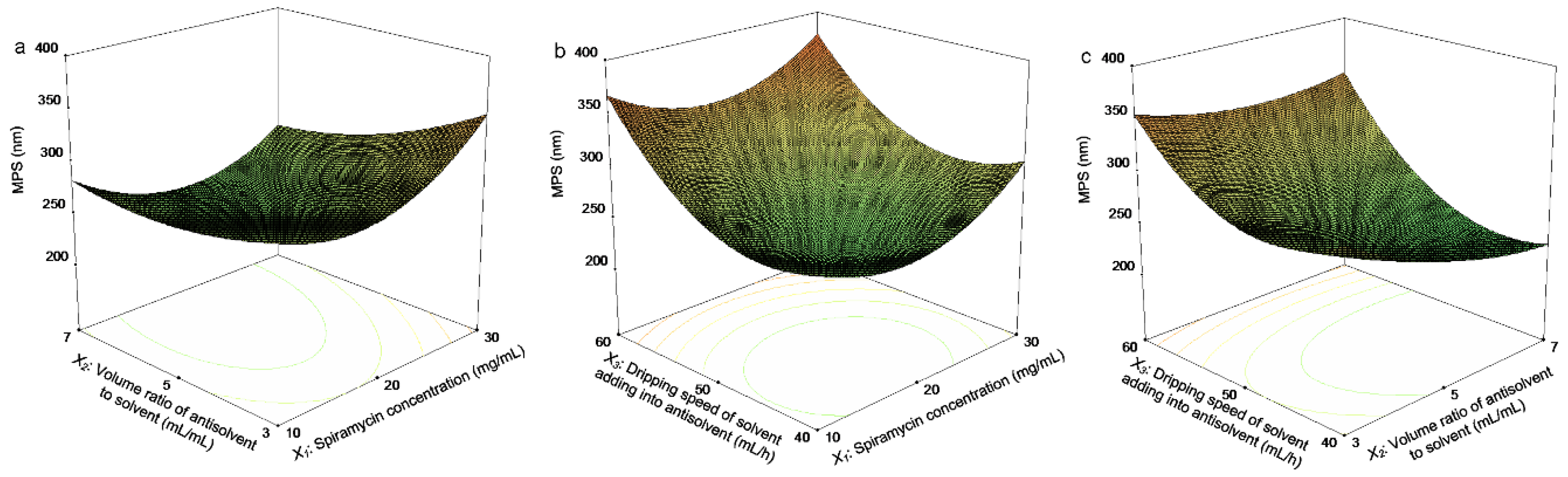



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




Antibacterial Inactivation Of Spiramycin After Titanium Dioxide Photocatalytic Treatment Sciencedirect




Neo Spiramycin I Cas 62 2 Glentham Life Sciences




Kegg Drug Spiramycin Adipate




Chemical Structure Of Obtained Spiramycin Derivatives Download Scientific Diagram




Monographie Spiramycine Adipate Stabilis 4 0
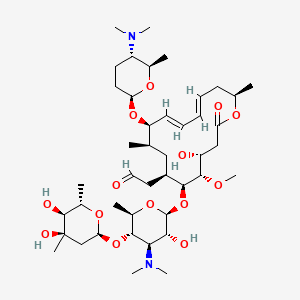



Spiramycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem



Pubs Acs Org Doi Pdf 10 1021 Acs Jmedchem 6b Rand 3dkrshtg




Spiramycin Structure C43h74n2o14 Over 100 Million Chemical Compounds Mol Instincts
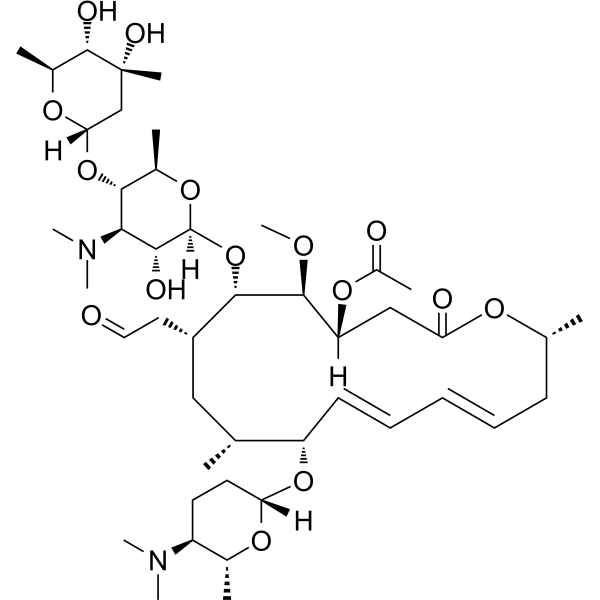



Acetylspiramycin Spiramycin B Macrolide Antibiotic Medchemexpress




Chemical Structures Of Main Components Of Spiramycin And Its Related Download Scientific Diagram




The Evolution Of Substrate Discrimination In Macrolide Antibiotic Resistance Enzymes Abstract Europe Pmc




Regulation Of The Biosynthesis Of The Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Journal Of Bacteriology
/D218B7AA3AA73D1B802585F8006742F1/$file/AS16859_structure.png)



Spiramycin I 50 5 Carbosynth Product




Effect And Mechanism Of Glycerol Addition On Spiramycin I Fermentation




Macrolides Ketolides Lincosamides Oxazolidinones 0 Ther Antibacterial Drugs




08 7 Spiramycin Embonate Antibiotic 799 Espiramicin Foromacidin Il 5902 Nsc Provamycin Rp 5337 Rovamicina Rovamycin Rovamycine Selectomycin Sequamycin Spiramycins Stomamycin C H N O Trc



Anti Obesity Effects Of Spiramycin In Vitro And In Vivo




Solution Conformations Explain The Chameleonic Behaviour Of Macrocyclic Drugs Danelius Chemistry A European Journal Wiley Online Library
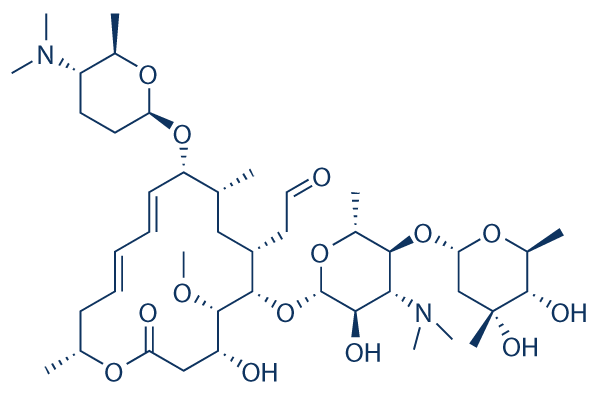



Spiramycin 99 Hplc Selleck Antibiotics Chemical



Spiramycin スピラマイシン Drug Approvals International
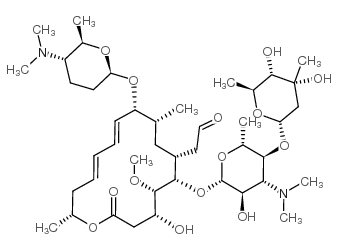



Spiramycin I Cas 50 5 Chemsrc



1




Rovamycin 3 000 000 Iu 10 Pcs




Spiramycin Adipate Cas 680 55 7 Chemsrc
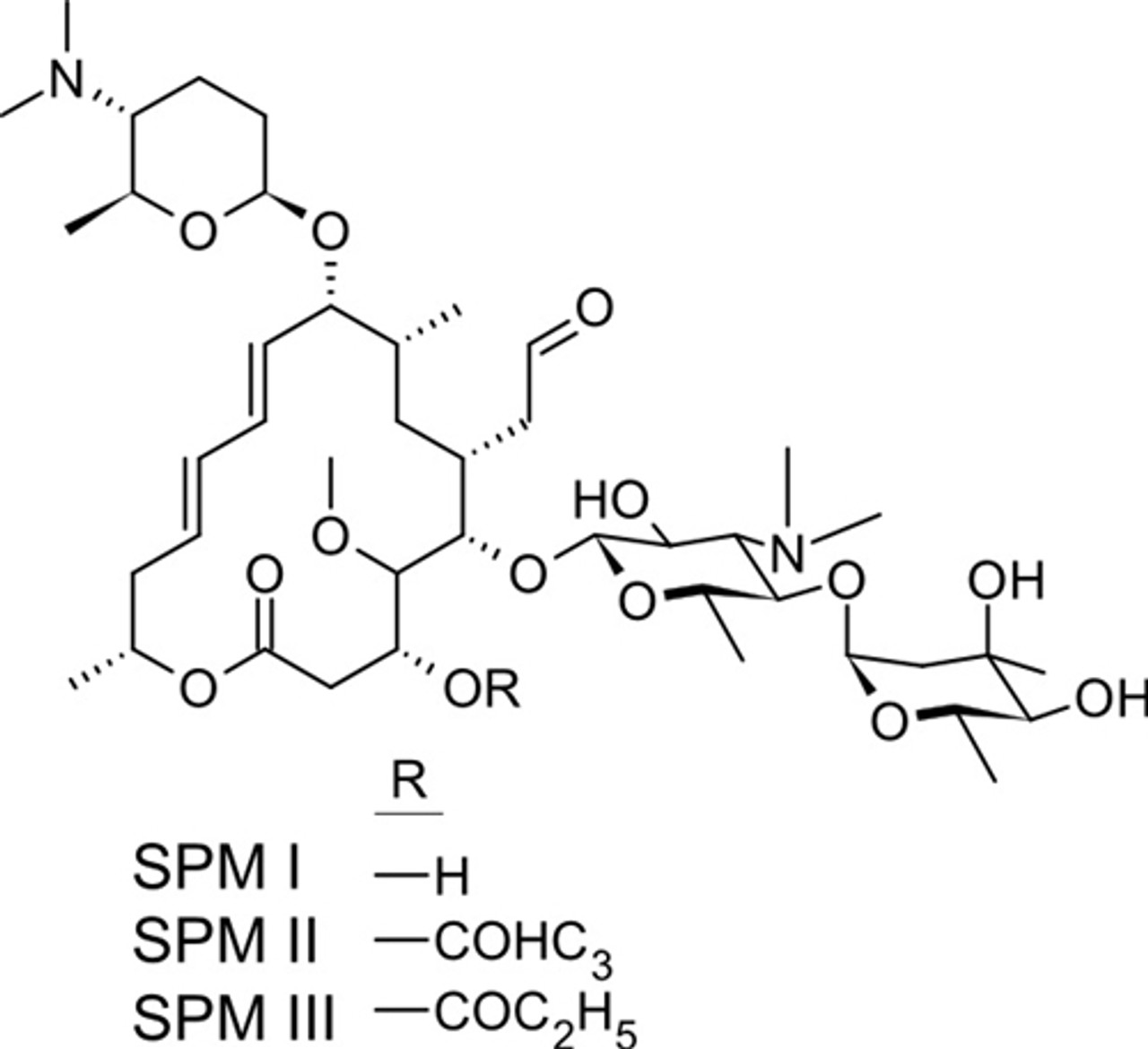



Spiramycin Toku E



Academic Oup Com Jac Article Pdf 42 5 572 4572 Pdf
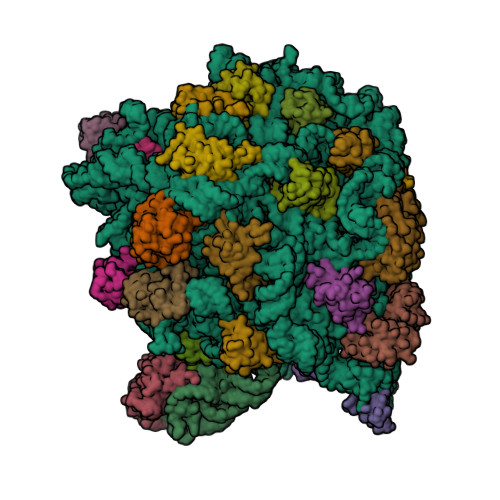



Rcsb Pdb 1kd1 Co Crystal Structure Of Spiramycin Bound To The 50s Ribosomal Subunit Of Haloarcula Marismortui



Q Tbn And9gcr9ohc8k8xdklq3 Vpmbg8 G8izttazf3lfsyvoxor 7xtdmk Usqp Cau
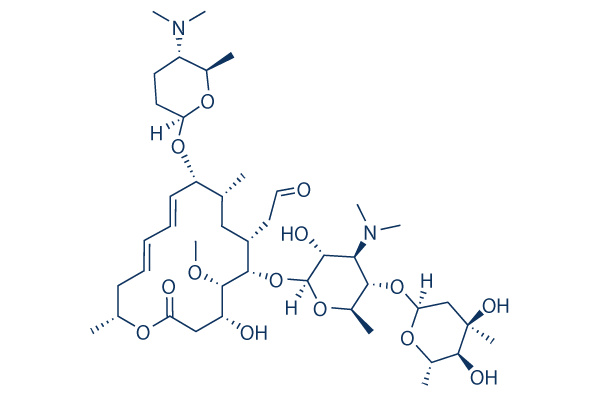



Spiramycin I 99 Hplc Selleck Antibiotics Chemical Qcfile




Spiramycin 8025 81 8 Tci Chemicals India Pvt Ltd




Spiramycin Goldbio



View Of A Novel Rp Hplc Method For The Detection And Quantification Of Clarithromycin Or Spiramycin In Bulk Drug Samples And Dosage Forms International Journal Of Pharmacy And Pharmaceutical Sciences
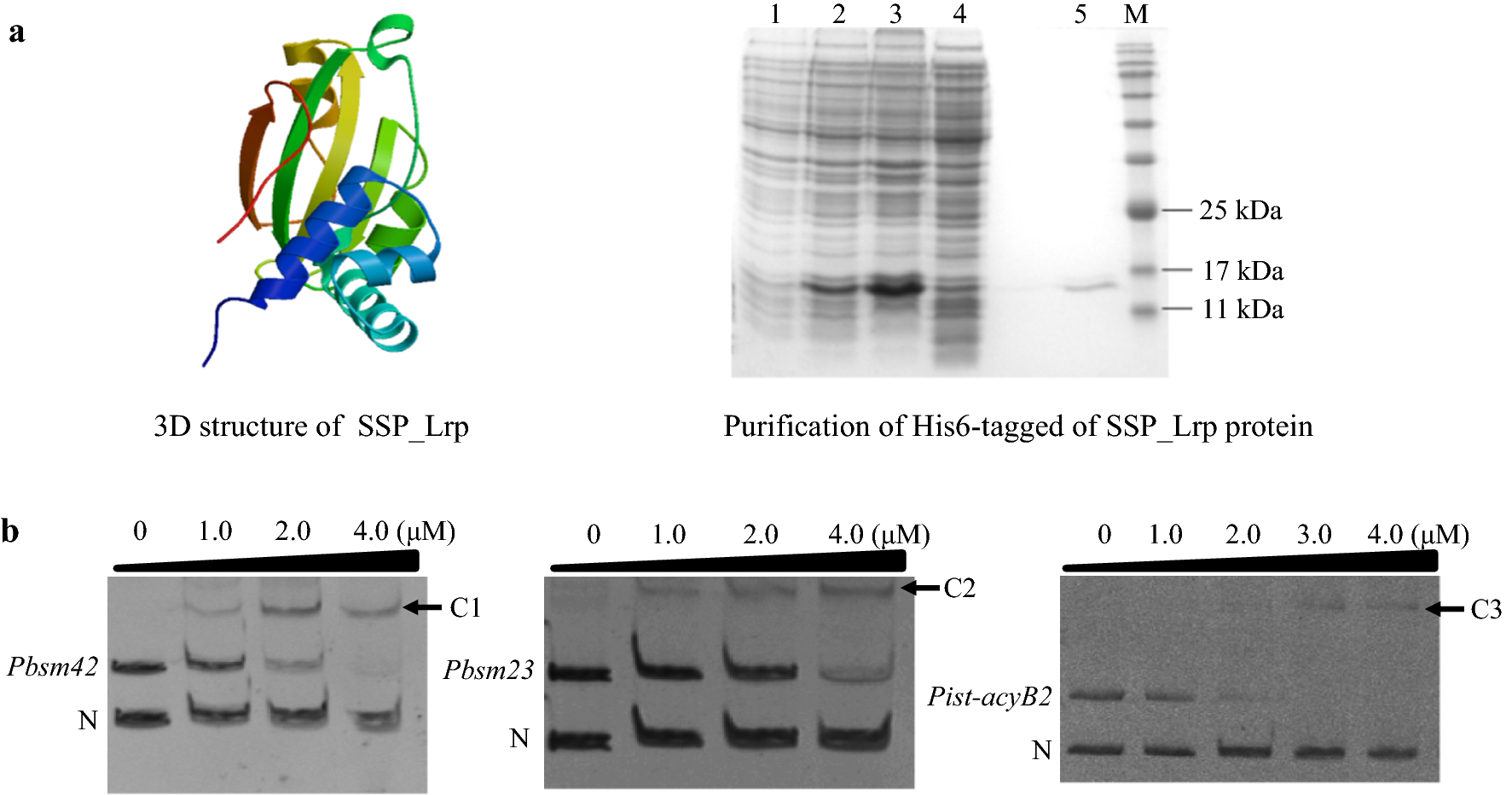



Engineering Of Leucine Responsive Regulatory Protein Improves Spiramycin And Bitespiramycin Biosynthesis Microbial Cell Factories Full Text
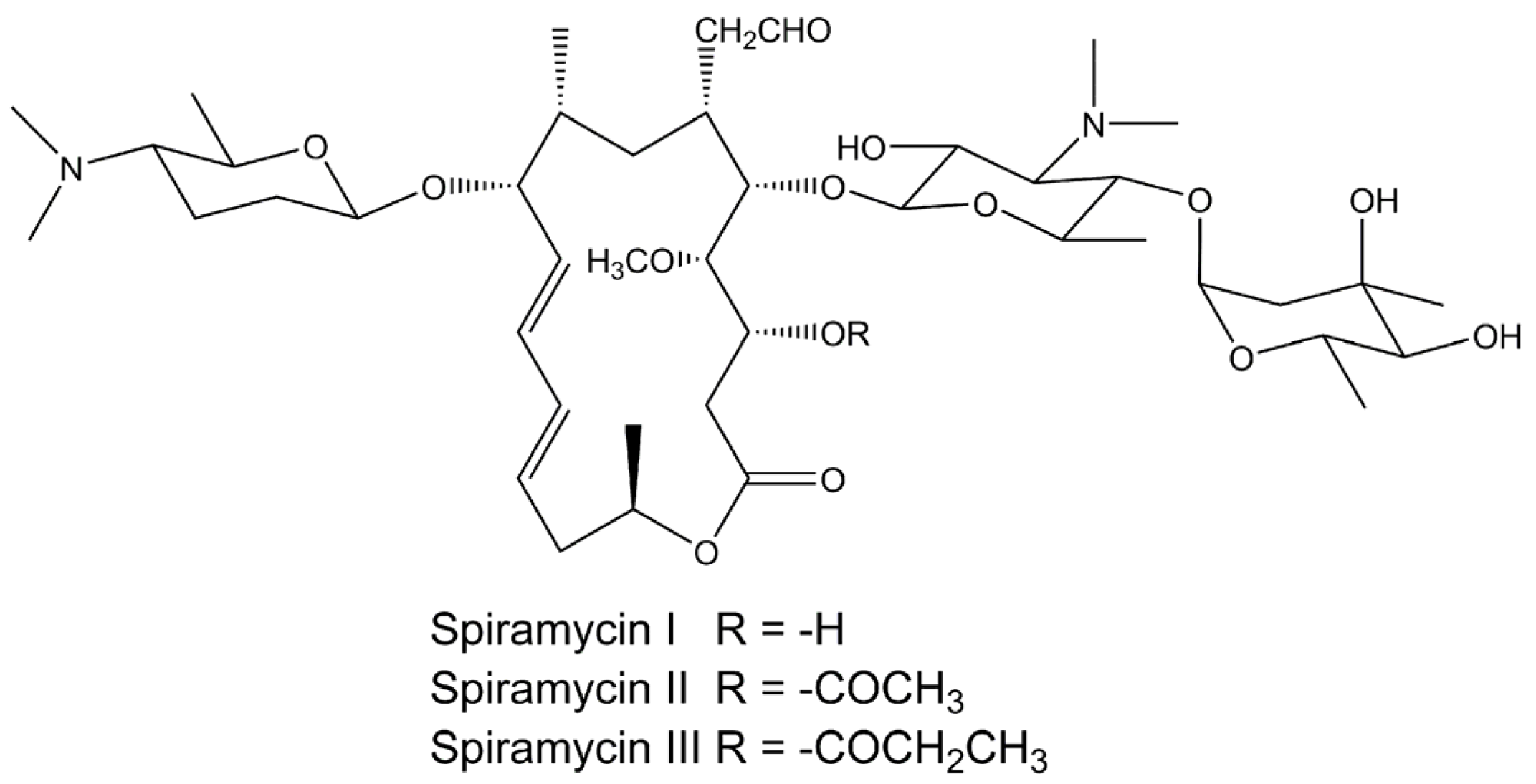



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




The Structures Of Four Macrolide Antibiotics Bound To The Large Ribosomal Subunit Sciencedirect
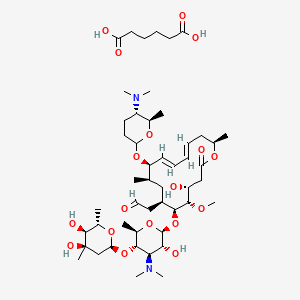



Spiramycin Adipate C49h84n2o18 Pubchem




Spiramycin Structure C43h74n2o14 Over 100 Million Chemical Compounds Mol Instincts




Epa1 Levoisovalerylspiramycin Iii And Preparations Preparation Methods And Uses Thereof Google Patents




Spiramycin Iii Cas 52 7




Spiramycin C43h74n2o14 Spiramycin I R H Bertin Bioreagent
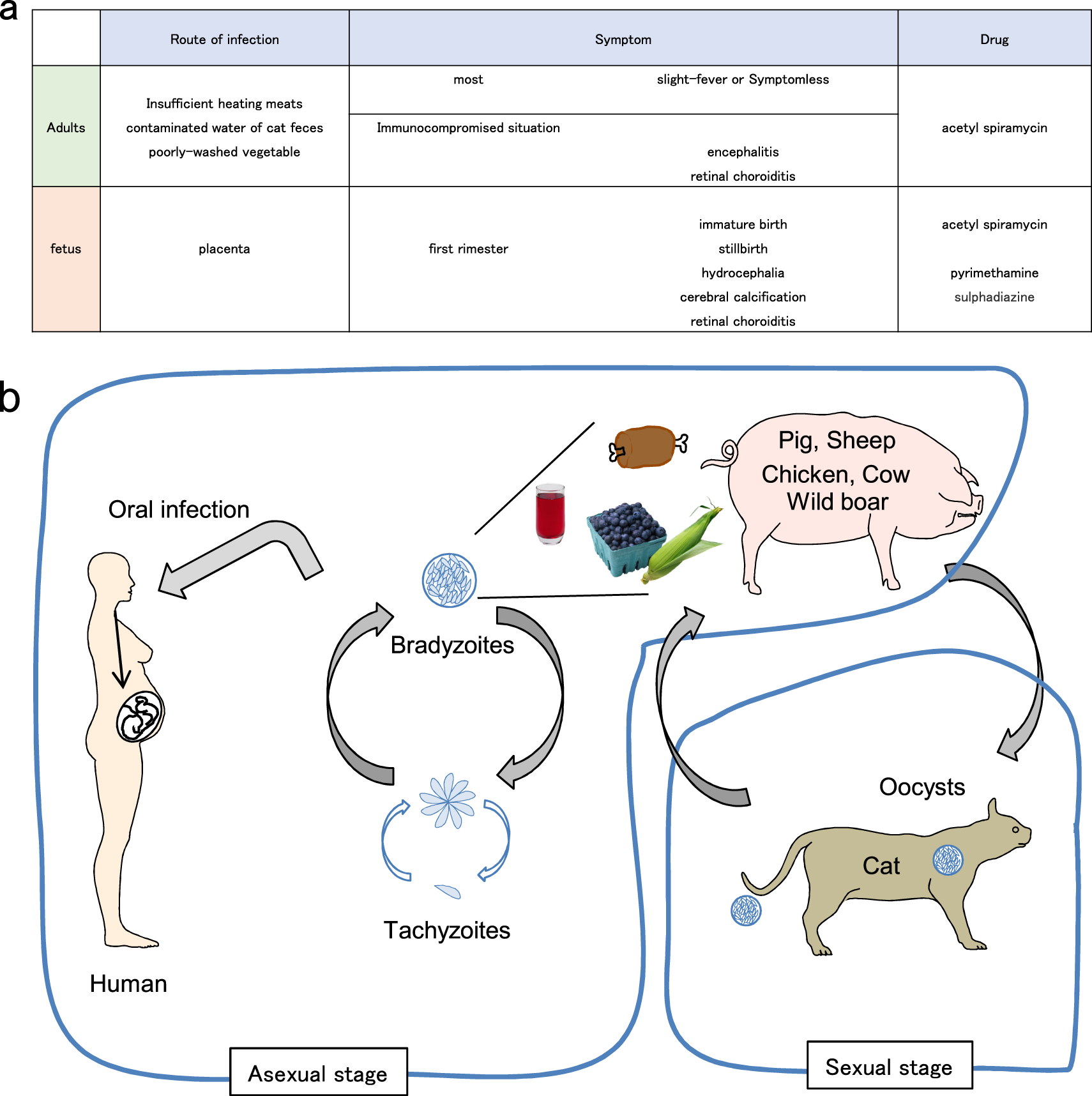



Innate Adaptive And Cell Autonomous Immunity Against Toxoplasma Gondii Infection Experimental Molecular Medicine



Www Ema Europa Eu Documents Mrl Report Spiramycin Summary Report 2 Committee Veterinary Medicinal Products En Pdf
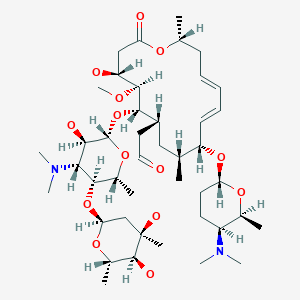



Spiramycin New Drug Approvals




Spiramycin I D3 Cas




Spiramycin Ii
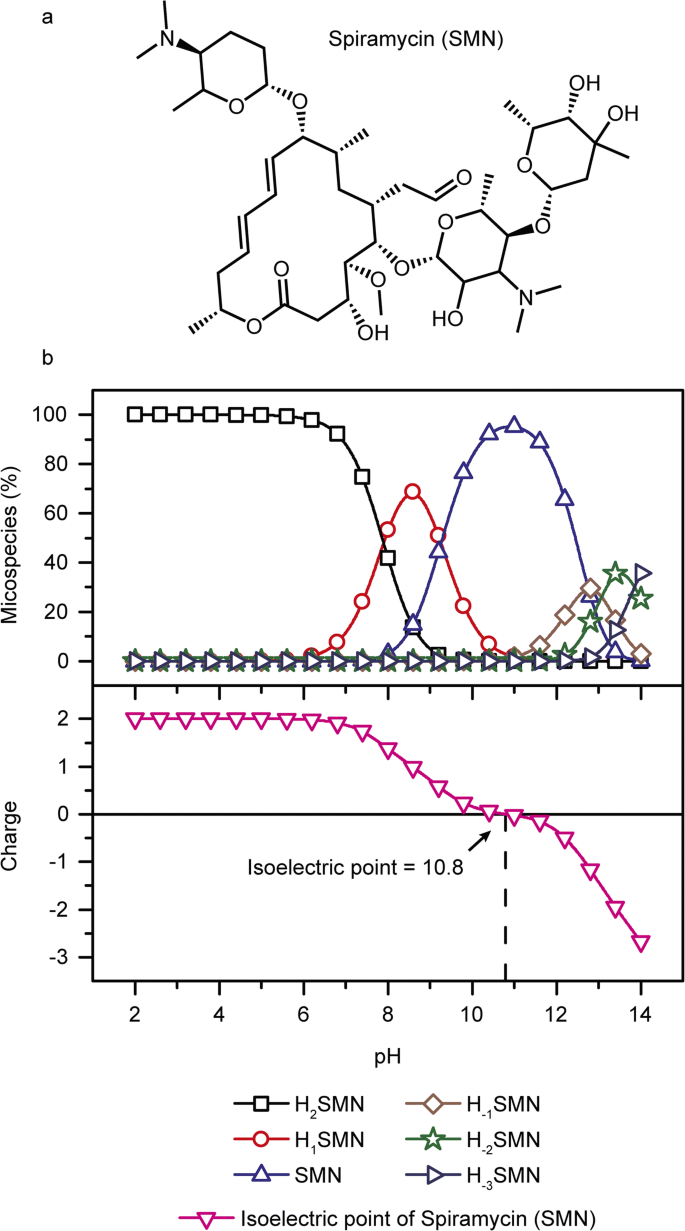



Spiramycin Adsorption Behavior On Activated Bentonite Activated Carbon And Natural Phosphate In Aqueous Solution Springerlink




Figure 3 Application Of Different Analytical Techniques And Microbiological Assays For The Analysis Of Macrolide Antibiotics From Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms And Biological Matrices



Www Scipress Com Ilns 47 1 Pdf




Figure 2 From Genome Mining Of Streptomyces Ambofaciens Semantic Scholar



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿